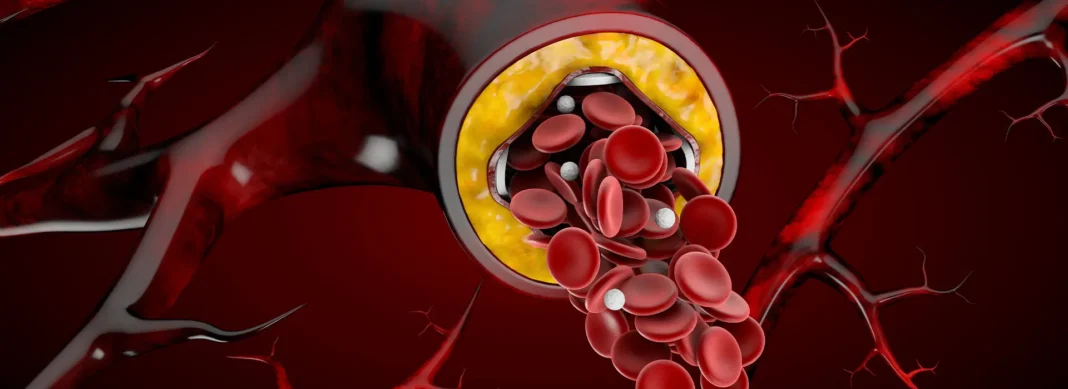
Hyperlipidemia, commonly known as high cholesterol, is a condition characterized by elevated levels of fats (lipids) in the blood. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and management strategies for hyperlipidemia is crucial for maintaining heart health and reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
What is Hyperlipidemia?
Hyperlipidemia occurs when there are abnormally high levels of cholesterol and/or triglycerides in the blood. These lipids can accumulate in the walls of blood vessels, leading to the formation of plaque and increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular complications.
Causes of Hyperlipidemia:
Hyperlipidemia can be caused by a combination of genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors. Family history, age, diet high in saturated and trans fats, sedentary lifestyle, obesity, diabetes, and certain medications can all contribute to elevated lipid levels in the blood. Additionally, some medical conditions such as hypothyroidism, kidney disease, and liver disease can also lead to hyperlipidemia.
Symptoms of Hyperlipidemia:
In many cases, hyperlipidemia does not cause noticeable symptoms until it leads to complications such as heart disease or stroke. However, some individuals may experience symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or leg cramps during physical activity. Routine blood tests, including a lipid panel, are often used to diagnose hyperlipidemia by measuring cholesterol and triglyceride levels in the blood.
Management and Treatment:
Managing hyperlipidemia typically involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medications, and regular monitoring. Lifestyle modifications may include adopting a heart-healthy diet low in saturated and trans fats, increasing physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and quitting smoking. Medications such as statins, fibrates, and cholesterol absorption inhibitors may be prescribed to help lower lipid levels in the blood. It’s essential for individuals with hyperlipidemia to work closely with their healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to their specific needs and risk factors.
Prevention and Prognosis:
Preventing hyperlipidemia involves adopting a healthy lifestyle early on, including maintaining a balanced diet, staying physically active, managing stress, and avoiding tobacco products. Regular screening and monitoring of lipid levels can help identify and manage hyperlipidemia before it leads to serious complications. With proper management and adherence to treatment recommendations, individuals with hyperlipidemia can reduce their risk of cardiovascular disease and improve their overall prognosis.
Conclusion:
Hyperlipidemia is a common condition that requires proactive management to reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and management strategies, individuals can take steps to maintain heart health and improve their overall well-being. With the right approach to lifestyle modifications, medications, and regular monitoring, it’s possible to effectively manage hyperlipidemia and lower the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Source – Cleveland clinic