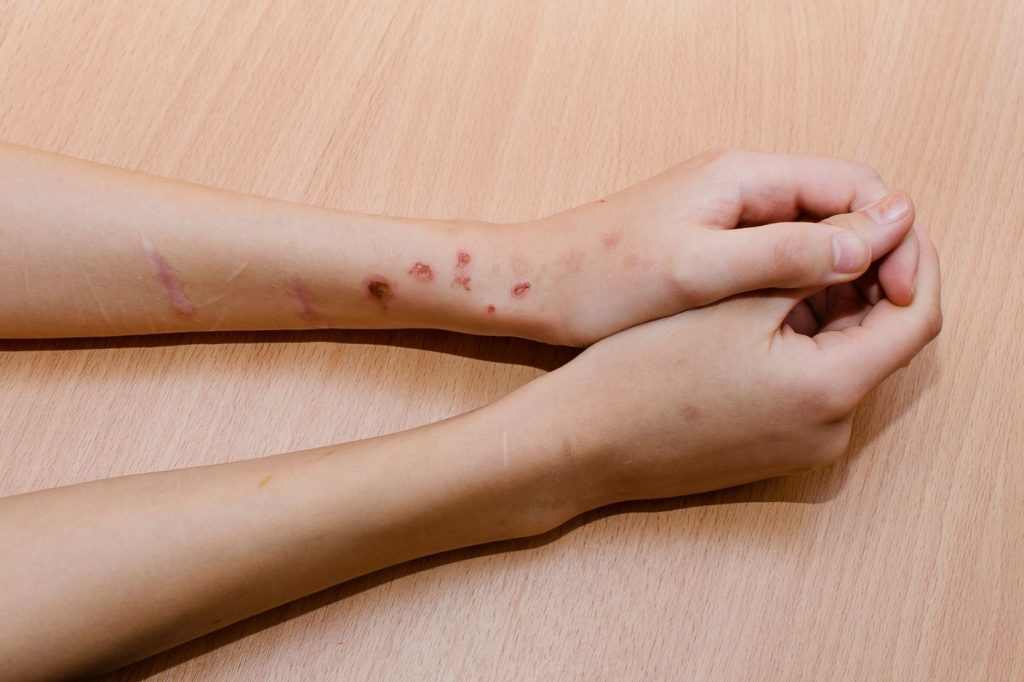
Self-harm, also known as self-injury or self-inflicted violence, is a complex behavior that can have serious physical and emotional consequences. Recognizing the causes, signs, and available support for individuals who engage in self-harm is crucial for intervention and recovery.
What is Self-Harm?
Self-harm refers to intentional, non-suicidal acts of harming one’s body, often as a way to cope with emotional pain, distress, or trauma. Common methods include cutting, burning, scratching, and hitting oneself.
Causes and Triggers:
Several factors may contribute to self-harm, including:
Mental health disorders: Depression, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and borderline personality disorder are commonly associated with self-harm.
Trauma and abuse: Past experiences of trauma, neglect, or abuse can increase the risk of self-injurious behavior.
Emotional dysregulation: Difficulty managing intense emotions or stressors may lead individuals to resort to self-harm as a coping mechanism.
Signs and Symptoms:
Signs that someone may be engaging in self-harm include:
Unexplained cuts, bruises, or burns on the body
Wearing long sleeves or pants, even in warm weather, to conceal injuries
Withdrawal from social activities or changes in mood and behavior
Expressing feelings of hopelessness, worthlessness, or guilt
Support and Treatment Options:
Seeking help for self-harm is essential for recovery and healing. Treatment options may include:
Therapy: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), and other forms of psychotherapy can help individuals learn healthier coping mechanisms and address underlying issues.
Medication: In some cases, antidepressants or mood stabilizers may be prescribed to manage associated mental health conditions.
Support groups: Peer support and group therapy provide opportunities for individuals to connect with others who have similar experiences and receive encouragement and understanding.
Prevention and Education:
Preventing self-harm requires a multifaceted approach that includes:
Education: Increasing awareness and understanding of self-harm among individuals, families, and communities can help reduce stigma and promote early intervention.
Risk assessment: Healthcare professionals play a crucial role in identifying individuals at risk for self-harm and providing appropriate support and resources.
Supportive environments: Creating safe and supportive environments where individuals feel comfortable seeking help and expressing their emotions is essential for preventing self-harm.
Conclusion:
Self-harm is a serious concern that requires compassion, understanding, and access to appropriate care and support. By recognizing the causes, signs, and available resources for individuals struggling with self-harm, we can work together to promote healing, resilience, and hope.
SEO Keywords: self-harm, self-injury, mental health, coping mechanisms, therapy, prevention, support, treatment options, emotional distress.
Source – Cleveland clinic